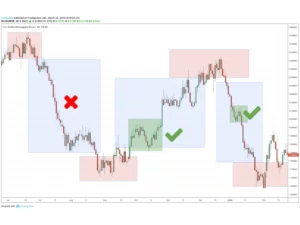
Forex trading is an example of selling one currency and purchasing another to profit from price movements. The market is available 24/5 across global centers, with daily volume in excess of $7.5 trillion. Beginners start with a demo account, learn the major pairs, and monitor news that moves rates.
Build skills with daily time on screen and strict guidelines. Master one or two pairs for months. Document each trade with entry reason, exit, and outcome. Fix errors on a weekly basis to turn practice into profit.
What Is Forex Trading?
Forex trading is the act of exchanging one currency for another, such as euros for US dollars, to profit from price differences. Prices move constantly throughout the day as global events, interest rates, and economic reports influence demand for currencies. It is the largest financial market, operating 24 hours a day with more than $6 trillion traded daily worldwide.
Market Sessions
- The trading cycle begins in Sydney, moves through Tokyo, then London, and ends in New York.
- The most active period is the London–New York overlap (13:00–17:00 GMT), where liquidity and volatility are highest.
- These hours offer tighter spreads and faster execution, making them ideal for short-term strategies.
Price Drivers
- Central banks adjust interest rates, directly affecting currency values.
- Economic reports such as employment, inflation, and GDP data often trigger sharp movements.
- Even a political statement or tweet can move major pairs like EUR/USD or USD/JPY by dozens of pips within minutes.
Understanding how global news and session timing affect price action helps traders identify better entry and exit points while maintaining control over market exposure.
Key Terms Every Beginner Must Know
Before trading real money, every trader should understand the basic terms used in forex. These concepts are the foundation of how trades work, how profits are calculated, and how risk is managed. Learning them early prevents costly mistakes and builds confidence when using trading platforms.
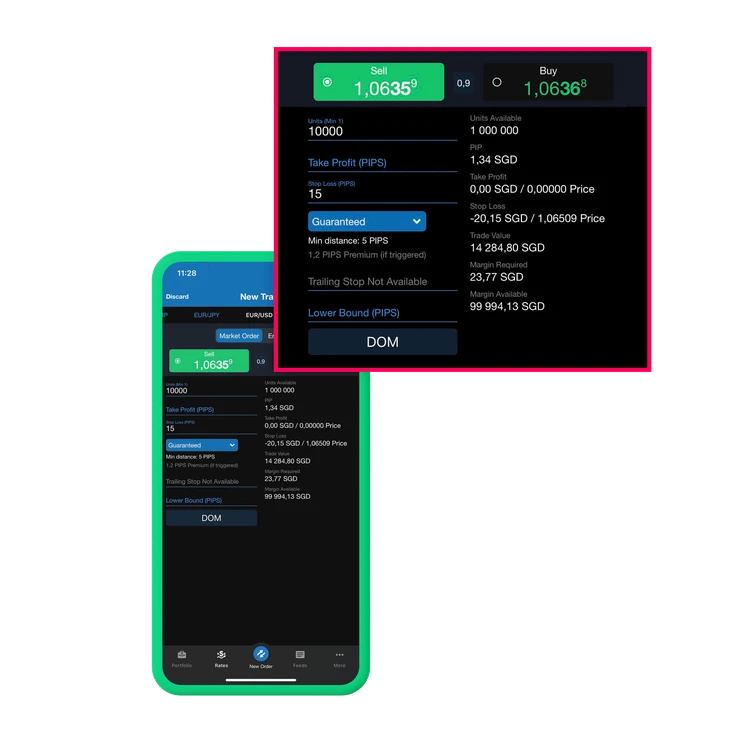
Memorize these and test yourself daily:
- Pip: The smallest price movement — 0.0001 for most currency pairs (e.g., EUR/USD).
- Lot: Standard trade size — 1 lot = 100,000 units, mini lot = 10,000, micro lot = 1,000.
- Spread: The difference between the buy (ask) and sell (bid) price — represents trading cost.
- Margin: The amount of money your broker holds to open and maintain a position.
- Leverage: A multiplier, like 1:50, meaning you control $50 for every $1 deposited.
- Stop-Loss: Automatically closes a trade at a set loss level to limit risk.
- Take-Profit: Automatically locks in profits when price hits a chosen target.
- Swap: A small overnight fee (or credit) for holding trades after 22:00 GMT.
Understanding these terms makes it easier to read charts, plan trades, and manage your account effectively. In practice, successful traders use these tools daily to protect capital and stay disciplined in changing market conditions.
Choosing a Reliable Broker
Picking a trustworthy broker is the first real step toward safe and consistent trading. Regulation should always come first — choose brokers licensed by FCA (UK), ASIC (Australia), or CySEC (Europe) to ensure fund protection and fair practices. Low spreads on major pairs like EUR/USD under 1 pip indicate a cost-effective setup for active traders. Avoid unregulated offshore brokers that promise unrealistic leverage or bonuses.
Must-Have Features
- Fast execution under 50ms for minimal slippage.
- Negative balance protection to prevent losses beyond deposits.
- Segregated client funds stored separately from broker capital for safety.
Quick Test Steps
- Deposit $100 demo funds to check transaction speed.
- Place 20 market orders during session opens (London/New York).
- Measure average execution time and spread consistency.
Reliable brokers maintain stable prices during volatile hours and execute trades without requotes. Testing before committing larger funds helps confirm transparency and platform performance in real conditions.
Understanding Currency Pairs
Forex trading is based on the exchange of one currency for another, displayed as base/quote. For example, if EUR/USD = 1.0900, it means 1 Euro equals 1.09 US Dollars. Understanding how pairs move helps traders plan better entries and exits. The first currency (base) is what you buy or sell, and the second (quote) shows its value in another currency.
Pair Types
- Majors: Include the USD with currencies like EUR, JPY, GBP, AUD, CAD, CHF, NZD.
- Minors: Pairs without USD, such as EUR/GBP or EUR/JPY.
- Exotics: Combine a major with an emerging market currency, like USD/TRY or EUR/ZAR.
Volatility Guide
| Pair | ||
|---|---|---|
| EUR/USD | 80 | London/NY |
| GBP/USD | 120 | London |
| USD/JPY | 90 | Tokyo/NY |
Volatility shows how much a pair moves daily. Majors like EUR/USD are stable and ideal for beginners, while GBP/USD or exotic pairs offer bigger moves but higher risk. Matching your trading strategy to pair volatility helps manage drawdowns and improve results over time.
Basic Trading Strategies
New traders should focus on mastering one simple system before adding complexity. Consistency comes from repetition — trade a single setup 200 times on demo before risking real money. This builds confidence and helps understand how price reacts in different conditions.
Pullback Entry Strategy
- Identify the daily high and low.
- Wait for the price to retrace about 50% into the day’s range.
- Enter after a candle closes above or below the midpoint.
- Place the stop-loss at the opposite end of the range.
- Set your target at the other side of the range for a clean exit.
This method works well in trending markets and helps avoid chasing price moves.
Scalping Setup
- Use a 5-minute chart with 9 EMA and 21 EMA indicators.
- Enter when the 9 EMA crosses the 21 EMA in the direction of the trend.
- Aim for a 10-pip profit with a 5-pip stop.
- Trade only during the first two hours of the London session, when liquidity is high.
Scalping teaches precision and patience. Stick to tight stops, trade during active hours, and avoid overtrading. With time and repetition, these basic systems help form a solid trading foundation.
Risk Management Rules
Risk control keeps traders in the game long-term. Every trade should have a defined loss limit to protect the account balance. Consistency in position sizing and discipline in following limits prevent emotional trading and large drawdowns.
Position Size Formula
Use this formula to calculate lot size based on your account and stop-loss:
Lots = (Risk $ ÷ Stop Pips) ÷ Pip Value
For a $5,000 account, risking $50 with a 20-pip stop and $1 pip value equals 0.25 mini lots.
Fixed Risk Per Trade
- $5,000 account = $50 max loss per trade (1%)
- $10,000 account = $100 max loss per trade (1%)
- Always define the amount before entering a position.
Weekly Cap Rule
- Maximum 5% total loss per week.
- If reached, stop trading until the next Monday.
- Review journal entries to identify what went wrong before resuming.
Applying these rules in daily practice builds account stability. Successful traders focus not on how much they can make but on how much they can afford to lose. Keeping losses small and consistent allows profits to grow naturally over time.
Technical Analysis Tools
Technical analysis helps traders identify market direction and timing using charts and indicators. The goal is to keep analysis simple and effective — too many tools can confuse signals. Focus on a few proven indicators that show trends and momentum clearly.
Keep charts clean. Max three indicators. Always combine them with price action and support/resistance levels for confirmation.
Trend Tools
- 50 SMA: Short-term trend direction.
- 200 SMA: Long-term trend indicator.
- Cross = signal: When 50 SMA crosses above 200, it’s a potential buy; below it, a potential sell.
Momentum Tools
- RSI (14): Below 30 = buy zone; above 70 = sell zone.
- Stochastic Oscillator: Similar to RSI but faster, ideal for short-term entries.
Practice Backtest
- Open the USD/JPY daily chart.
- Scroll back 6 months in history.
- Mark every 50/200 SMA crossover.
- Count pips to the next 50-pip move for accuracy testing.
This simple backtesting method helps measure signal reliability and refine strategy timing. Practicing regularly builds pattern recognition, which improves decision-making and consistency in live trading.
Fundamental Analysis Basics
Fundamental analysis focuses on understanding how global economic factors influence currency prices. Traders use news, reports, and key data releases to predict market direction. Tracking major events helps you plan trades and avoid unexpected volatility.
Follow the economic calendar daily to stay informed about news that moves markets. Pay attention to central bank meetings, employment reports, and inflation data — these are the biggest market movers.
High-Impact Events
| Event | Schedule | Time (GMT) |
|---|---|---|
| US Non-Farm Payroll | First Friday of each month | 13:30 |
| Fed Rate Decision | Every 6 weeks | 19:00 |
| CPI Inflation | Mid-month | Varies |
Safe News Rule
- Avoid trading 15 minutes before and after red-folder events (high volatility).
- Close or reduce open positions before releases.
- Wait for market reaction to stabilize before re-entering.
Understanding these fundamentals improves timing and risk management. In practice, successful traders build their week around news schedules — trading active sessions and avoiding unpredictable spikes.
Practice Tips for Faster Progress
Building trading consistency takes discipline and routine. Practicing on a demo account like it’s real money helps develop emotional control and technical accuracy. Stick to a structured plan and measure your progress week by week instead of chasing fast profits.
60-Day Bootcamp
| Week | Focus | Goal |
|---|---|---|
| 1-2 | EUR/USD only | 50 trades |
| 3-4 | Add GBP/USD | 100 trades total |
| 5-6 | Live micro, $200 | 1% monthly gain |
| 7-8 | Journal review | Cut losers 20% |
Daily Routine
- Check calendar at 07:00 GMT.
- Mark levels on 1H chart.
- Trade 08:00–12:00.
- Log results by 13:00.
Following a plan like this helps traders develop habits that lead to steady improvement. Reviewing your journal regularly reveals weak spots and guides adjustments. Over time, consistency in practice transforms into real trading confidence and profit stability.
FAQ
Is $100 enough to start forex?
Yes, $100 is enough to start trading using micro or cent accounts. It won’t generate big profits, but it helps you learn position sizing, money management, and emotional control. Choose a regulated broker that allows 0.01-lot trading and low minimum deposits.