Forex trading means exchanging one currency for another to make a profit from price movements. Traders buy currencies they believe will rise in value and sell those expected to fall. The forex market runs 24 hours a day, five days a week, with no central exchange — all trades happen electronically through brokers.
A trader might buy EUR/USD at 1.0900 and sell at 1.0950, making 50 pips of profit. The key to success is learning how prices move, when to trade, and how to manage risk. With proper tools, discipline, and a clear plan, forex can be treated like a business rather than a gamble.
How Forex Trading Works in Practice
Forex trading happens through brokers who connect traders to global liquidity providers. You trade in pairs, such as EUR/USD, where one currency is bought, and another is sold. The price reflects how much of the quote currency (USD) you need to buy one unit of the base currency (EUR).
If EUR/USD = 1.1000 → 1 Euro costs 1.10 USD.
When the rate increases to 1.1050, your Euro becomes more valuable, and selling it gives you profit.
| Action | Pair | Price | Result |
|---|---|---|---|
| Buy | EUR/USD | 1.1000 | Entry |
| Sell | EUR/USD | 1.1050 | +50 pips profit |
Profit = (Price change × lot size × pip value).
Controlling risk per trade is essential — small consistent gains add up faster than big, risky bets.
Step 1: Understanding Market Sessions
The forex market is divided into four major sessions — Sydney, Tokyo, London, and New York. Liquidity and volatility depend on which sessions overlap.
Session Timetable (GMT)
| Session | Time (GMT) | Activity Level |
|---|---|---|
| Sydney | 22:00 – 07:00 | Low |
| Tokyo | 00:00 – 09:00 | Medium |
| London | 08:00 – 17:00 | High |
| New York | 13:00 – 22:00 | Very High |
The London–New York overlap (13:00–17:00 GMT) offers the best trading opportunities due to high liquidity and tighter spreads.
Step 2: How Brokers Execute Trades
Brokers connect traders to the market using platforms like MetaTrader 4 (MT4) or cTrader. Orders are filled either through market execution or instant execution, depending on broker type.
- ECN brokers send trades directly to liquidity providers with tight spreads and small commissions.
- Market makers act as counterparties, offering fixed spreads and faster fills for small accounts.
Always check for regulation (FCA, ASIC, CySEC) and negative balance protection before depositing.
Step 3: Margin, Spread, and Pip Explained
- Margin is the amount required to open a trade.
- Spread is the difference between buy and sell prices — your trading cost.
- Pip measures the smallest price movement, usually 0.0001 for most pairs.
If you trade 1 mini lot (10,000 units) on EUR/USD, one pip equals $1.
A 20-pip profit = $20.
Margin allows traders to control large positions with small deposits, but misuse can cause losses.
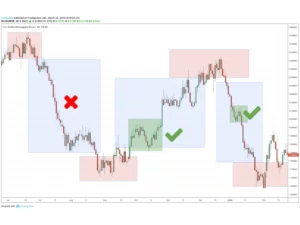
Step 4: Reading Charts and Indicators
Price charts show historical and current market movement. Use indicators to spot trends or reversals.
Basic Tools:
- 50 SMA (Simple Moving Average): Short-term trend.
- 200 SMA: Long-term direction.
- RSI (14): Overbought above 70, oversold below 30.
- MACD: Measures momentum and crossovers for entry signals.
Stick to two or three indicators max — clarity beats complexity.

Step 5: Managing Risk and Setting Goals
Never risk more than 1–2% of your account per trade. Use stop-loss and take-profit orders to automate exits. Keep a trading journal to track performance and emotions.
- Account balance: $1,000
- Risk: 2% → $20 per trade
- Stop-loss: 20 pips → lot size = 0.1 mini lot
Small risk keeps you in the game longer, letting experience build confidence.
Step 6: Developing a Trading Strategy
Every trader needs a plan based on time availability, style, and capital.
Main Styles:
- Scalping: Short trades, 5–10 pips profit.
- Day Trading: Same-day entries and exits.
- Swing Trading: Holding for days or weeks.
- Position Trading: Long-term trend following.
Backtest your strategy using demo accounts for at least 100 trades before going live.
Step 7: How Profits and Losses Are Calculated
Your profit depends on pip movement, lot size, and pair volatility.
- 1 pip on a 1 standard lot = $10.
- If EUR/USD moves 50 pips in your favor → $500 profit.
- Use calculators or MT4’s trade tab for quick tracking.
Losses are part of trading — consistency matters more than accuracy. A 60% win rate with good risk/reward can be profitable.
Step 8: Continuous Learning and Practice
Markets change, so traders must adapt. Keep studying economic news, technical setups, and psychology. Join communities or forums for peer feedback, but rely on your own testing. Review results weekly to refine performance. Success in forex comes from discipline, risk control, and steady practice, not luck.
FAQs
How much money do I need to start?
You can start with $100–$200 using micro or cent accounts. Focus on learning, not profits.